Introduction
The Goods and Services Tax (GST) regime in India has significantly transformed the country's taxation system, simplifying and unifying various indirect taxes. Under GST, it is crucial for businesses to comply with the regulations and procedures laid out by the government. One important aspect of GST compliance is the concept of an "Additional Place of Business". In this comprehensive blog, we will delve into what an additional place of business is in the context of GST, its significance, registration requirements, and the procedures businesses need to follow to ensure compliance.
Want VPOB or APOB for Your Business? Contact us Today!
Lowest Rates | 100% GST Approval | APOB Addition
Chat on WhatsAppWhat is Additional Place of Business in GST?
Before we dive into the specifics, let's establish a clear understanding of what an additional place of business under GST.
An additional place of business refers to any location other than the principal place of business where a registered person conducts business activities. It essentially implies any branch, warehouse, godown, factory, office, or any other establishment where taxable goods or services are supplied or offered. It is vital to note that the principal place of business is the primary location from which a business operates and is usually the place mentioned in the GST registration certificate.
Businesses often have multiple locations or branches across different cities or states, and each of these locations can be considered an additional place of business. These additional places of business may have different addresses, but they are part of the same legal entity, and their activities are subject to GST regulations.
Reasons for Adding Additional Place of Business in GST
Understanding the significance of adding and registering additional places of business is essential for GST compliance and smooth business operations. Here are some key reasons why it is crucial:
-
Legal Compliance: Under the GST law, if a business is operating in more than one place, apart from its principal place of business, under the same GST registration, then they need to add their other business places as additional places of business under GST. Failure to do so can lead to non-compliance and legal consequences.
-
Input Tax Credit (ITC): Accurate registration of additional places of business allows businesses to claim input tax credit on the GST paid for goods and services used at these locations. This ensures businesses can offset their tax liabilities effectively.
-
Tax Liability: Each additional place of business may have different tax liabilities, and the registration helps in determining the correct tax obligations for each location. This is particularly important for businesses operating in multiple states, as they must adhere to state-specific GST regulations.
-
Ease of Compliance: Registering additional places of business streamlines the compliance process. It allows businesses to file GST returns, maintain records, and pay taxes for each location separately, making it easier to manage tax-related responsibilities.
-
Avoiding Penalties: Non-compliance with GST regulations can result in hefty penalties. By registering additional places of business, businesses can avoid such penalties and fines.
List of Required Documents for Additional Place of Business
To add an additional place of business in the Goods and Services Tax (GST) system, you typically need the following documents:
- Proof of Address : Documents such as a rental agreement, lease agreement, or utility bill for the additional place of business.
- Ownership Proof: If you own the property, documents like property papers, title deed, or possession letter are required.
- NOC (No Objection Certificate): If the property is rented, you might need an NOC from the landlord acknowledging the use of the premises for business purposes.
- GST Registration Certificate: Copy of the existing GST registration certificate.
- Authorization Letter: A letter of authorization from the primary place of business authorizing the operation of the additional place of business.
- Bank Details: Bank account details of the additional place of business.
- ID and Address Proof: ID and address proof of the authorized signatory.
How to Add Additional Place of Business in GST Portal
Follow this Step-by-Step Process to Add Additional Place of Business in GST
Step 1: Access the GST Portal
- Visit the official GST portal: https://www.gst.gov.in/
- Log in to the GST portal using your user ID and Password.
Step 2: Navigate to Registration Section
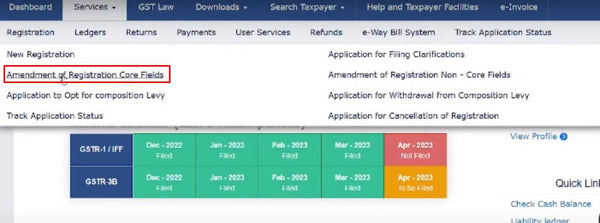
Once logged in, locate the "Services" menu and select the "Registration" option, and click on the "Amendment of Registration Core Fields" option.
Step 3: Access the APOB Registration Form
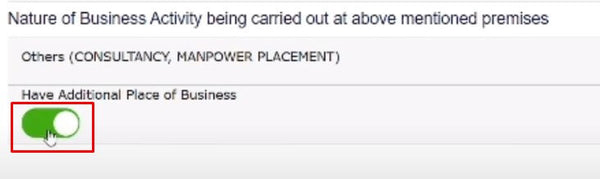
In the next window, click on the principal place of business section and go to the button and turn on the toggle button of "have additional place of business". click on save and continue button at right bottom corner. after doing this you can your additional place of business.
Step 4: Enter the number of APOBs You Want to Add
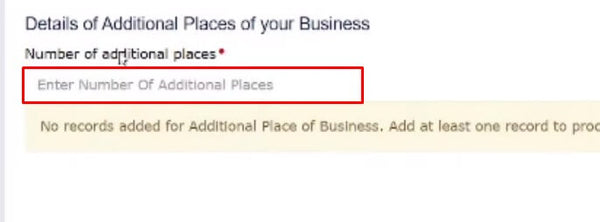
Once you complete the above step, you will be asked to enter the number of APOBs you want to add. Enter the number as desired. Once you enter the number, a new button in the bottom right corner will be enabled. Click on that button.
Step 5: Fill out the APOB details
In the next window, you will be required to fill out the APOB details such as pin code, state, district, road, building number, etc. Fill out all the required fields carefully.

Step 6: Specify the premise ownership and Upload the proof of address
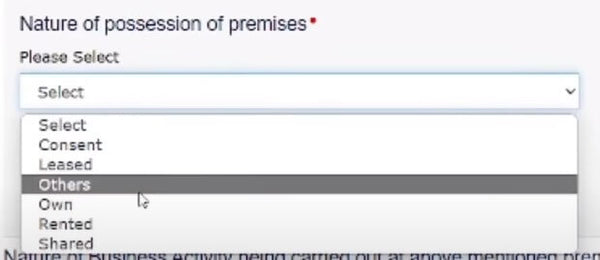
Once you have filled out the required details, scroll down a bit until you find the option "nature of possession of premises." Here, you have to select the option that corresponds to the premise ownership, such as owned, leased, rented, etc.
After specifying the premise ownership, you need to upload the proof of premises. Please ensure that you upload documents in the suggested format and size only.
Step 7: Provide the Proof of Address
After completing the above step, you have to upload the proof of additional place of business.
Note: you can upload documents in either JPEG or PDF format only other formats are now allowed.
Step 8: Select the Business Activity Type and Provide the Reason
After uploading the documents, scroll down a bit and you will see multiple checkboxes. Here, you have to select the business activity you are going to conduct at that additional place of business premises. For example, if you want to use that additional premises for storage, you can check the option of "warehouse". Carefully check the option that corresponds to the type of business activity you are going to conduct there.
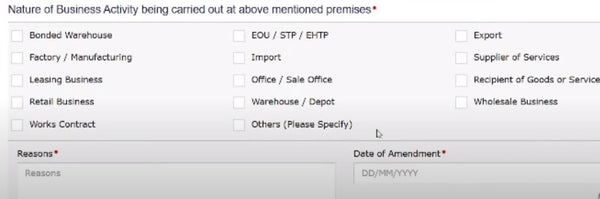
After selecting the option, enter the reason for using the additional place of business and enter the date of amendment. Then, click on the "save and continue" button. After this, the APOB details will be successfully saved.

Step 9: Final Verification
After saving the details, click on the continue button in the right corner. After this, you have to complete the verification. Select the authorized signatory and complete the verification with DSC or EVC method. With the DSC method, you can complete verification using a digital signature, and with EVC, you can complete verification using an OTP sent to the authorized signatory's mobile number.
Step 10: Checking Approval Status
Once the application is successfully submitted, the system will verify it. Within 15 minutes, you will receive a message on your registered email and mobile number containing an application reference number (ARN) which you can use to track the status of your APOB application.
Common Challenges and Solutions
While registering additional places of business under GST is essential, it can be a complex process. Here are some common challenges and possible solutions:
Challenge 1: Lack of Awareness
- Solution: Businesses should invest in training and educate their finance and accounting teams about GST compliance requirements, including the registration of additional places of business.
Challenge 2: Documentation Errors
- Solution: Ensure that all required documents are accurate and up to date. Seek professional assistance if needed to avoid documentation errors.
Challenge 3: Complex Business Structures
- Solution: For businesses with complex organizational structures, consulting with GST experts or tax advisors can help ensure correct registration for each additional place of business.
Challenge 4: Regulatory Changes
- Solution: Stay updated with any changes in GST regulations or compliance requirements. This can be achieved by regularly checking official government sources or subscribing to newsletters from reliable tax consultants.
Conclusion
In the era of GST, compliance with tax regulations is of utmost importance. Understanding what constitutes an additional place of business and how to register these locations under GST is crucial for businesses aiming to operate smoothly while adhering to the law.
Businesses should not view GST compliance as merely a legal obligation but as a means to benefit from simplified taxation, input tax credits, and smoother business operations. By ensuring the proper registration of additional places of business and fulfilling all GST-related requirements, businesses can thrive in the new era of taxation in India.
The concept of additional places of business in GST is an integral part of GST compliance. It encompasses all the physical locations from which a registered business operates. Registering these additional places correctly, following the stipulated process, and ensuring compliance with GST regulations are essential for any business looking to thrive in the GST era.
Furthermore, it's important to understand that while businesses may have multiple branches or locations, each additional place of business should be registered separately under GST, and compliance should be maintained on a per-location basis. This ensures that the tax obligations and benefits are appropriately managed across all the places where business activities are conducted.
Additional Resources:
Learn how to file an Appeal - https://www.gst.gov.in/help/appeal
How to Register Using DSC or EVC - https://www.gst.gov.in/help/loginanddsc
FAQs-
1. How to check GST additional place of business?
Log in to the GST portal and check the "Place of Business" section in the taxpayer’s profile.
2. What is the penalty for not declaring an additional place of business in GST?
A penalty of up to ₹25,000 under Section 125 of the CGST Act may apply.
3. What is Form REG-14 for GST?
Form REG-14 is used to amend GST registration details, including business addresses.
4. Can I add an additional place of business in GST?
Yes, by submitting Form REG-14 on the GST portal.
5. How do I add another business to my existing GST?
Add the new business location as an additional place of business via Form REG- 14.
6. Can I run two businesses under one GST?
Yes, if both operate under the same PAN and legal entity.
7. What documents are required for place of business in GST?
Proof of ownership, utility bills, rent agreements, or consent letters are required.
8. Is it mandatory to add an additional place of business in GST?
Yes, all business premises must be declared under GST.
9. What is the time limit to update an additional place of business in GST?
It should be updated as soon as the new location becomes operational.
10. What is Section 130 of the GST penalty?
Section 130 imposes penalties for tax evasion, including confiscation of goods or conveyances.















